Creating/editing Patch Management policies
NAVIGATION Modules > Patch Management
PERMISSIONS Patch > Edit Policy
VSA 10's Patch Management module enables you to create policies capable of delivering OS updates and third-party applications to your managed endpoints.
This article describes the process to deploy software to a managed device.
NOTE For comprehensive information about how policies work, refer to Policies overview. To learn how to automate your patch review process, consult Automating patch review. For details about managing software on a macOS computer or iOS/iPadOS mobile device, review VSA 10 MDM: Apple MDM profiles.
Patch Management overview
Patch Management is a strategy for managing patches or upgrades for software applications and technologies. A patch is software designed to update a computer program or its supporting data to fix or improve it. This includes fixing security vulnerabilities and other bugs and improving the usability or performance.
Effective patch management protects devices against known vulnerabilities that attackers could exploit, and is an essential component of any cybersecurity strategy.
Patch Management brings the following benefits to a customer's IT environment:
- Security: Patch Management is vital for correcting security flaws. Many patches address vulnerabilities that could be exploited by hackers to gain unauthorized access to devices. By promptly applying these patches, a customer can significantly reduce the risk of a security breach.
- Compliance: Many industries are governed by regulatory standards that require companies to maintain certain levels of cybersecurity. Patch Management ensures that devices are up to date and compliant with these regulations.
- Performance improvements: Aside from security updates, patches can also bring enhancements that improve the performance of software and devices, leading to better efficiency and user experience.
- Access to new features: Software updates can deliver new features and improvements that are not available in earlier versions, allowing users to take advantage of the latest functionalities.
Patch Management is a systematic process involving several steps to ensure that software updates and patches are consistently applied to computers and network equipment. As follows is a general outline of how it works:
- Inventory: Assess inventory of the software on devices to understand what applications and versions are in use. This helps in identifying which patches are applicable.
- Patch discovery: Regularly check for new patches and updates released by software vendors. This can be done manually or automatically with patch management tools.
- Risk assessment: Evaluate the patches to determine the urgency of applying them based on the severity of the issues they address. This might involve understanding the vulnerabilities and the potential impact on the business.
- Prioritization: Decide which patches to apply first, often based on the risk assessment. Critical security patches are usually prioritized over routine updates.
- Testing: Test patch deployment in a controlled environment to ensure it does not cause issues with existing devices or applications before deploying a patch widely.
- Approval: Approve patches for deployment. In some organizations, this step requires sign-off from IT management or compliance officers.
- Deployment: Roll out the patches to the relevant devices. This can be done manually but is often automated using patch management software. The deployment may be staged across different parts of the network or done all at once, depending on the organization's size and structure.
- Verification and monitoring: Confirm that patches have been applied correctly, and monitor devices for any unexpected behavior that might indicate a problem with the patch.
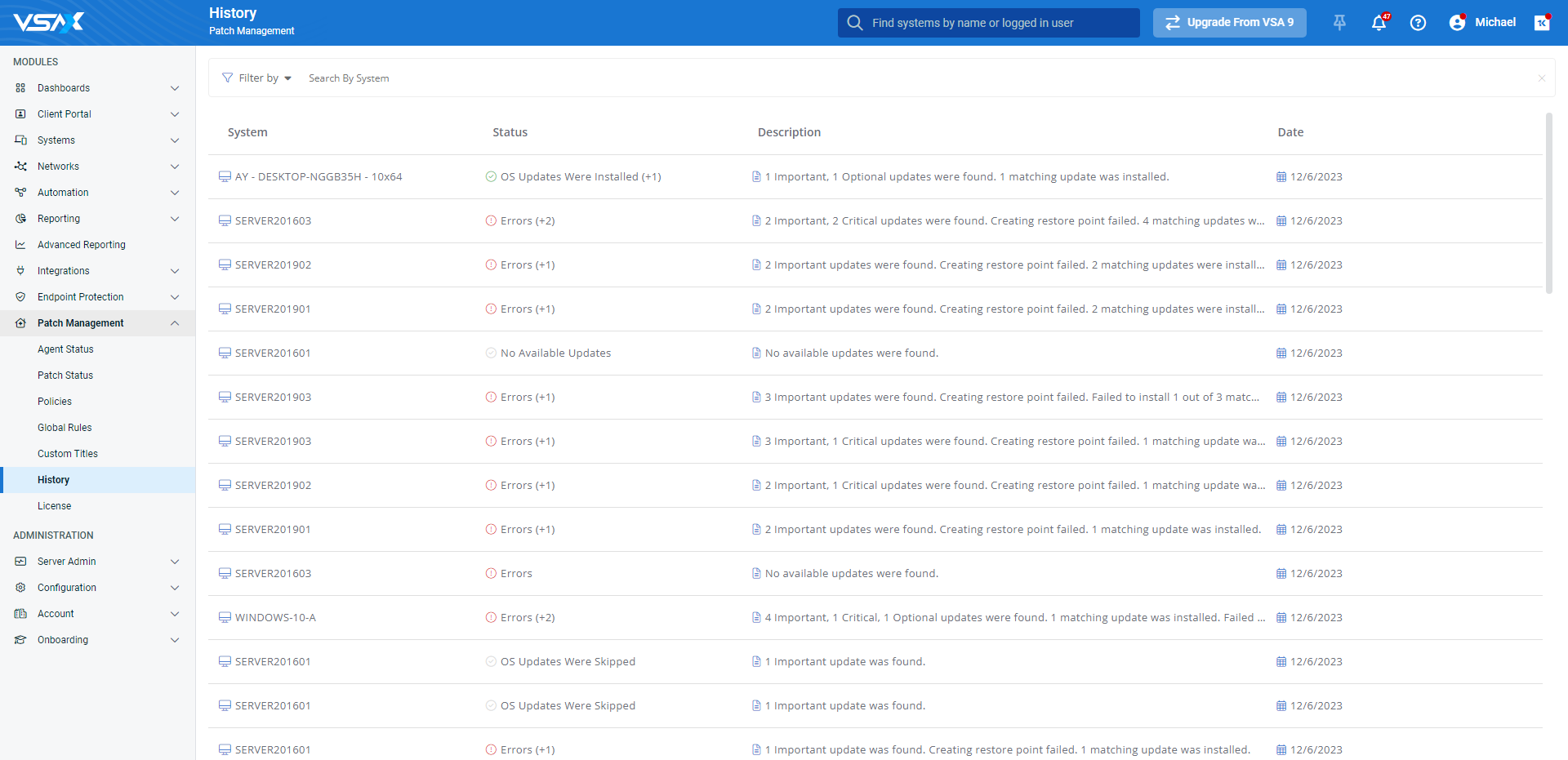
- Documentation and reporting: Record all patch management activities, including what was patched, when, and the outcome. This documentation is crucial for audits, compliance, and troubleshooting future issues.
- Maintenance: Continuously monitor for new patches and updates and maintain the tools and devices used for patch management.
To manage device updates and third-party software on your devices using VSA 10, first create a patch policy. Then, assign the patch policy to a specific device, scope, agent or tag group.
How to...
- From the left navigation menu in VSA 10, navigate to Patch Management > Policies.
- Click Create Policy.
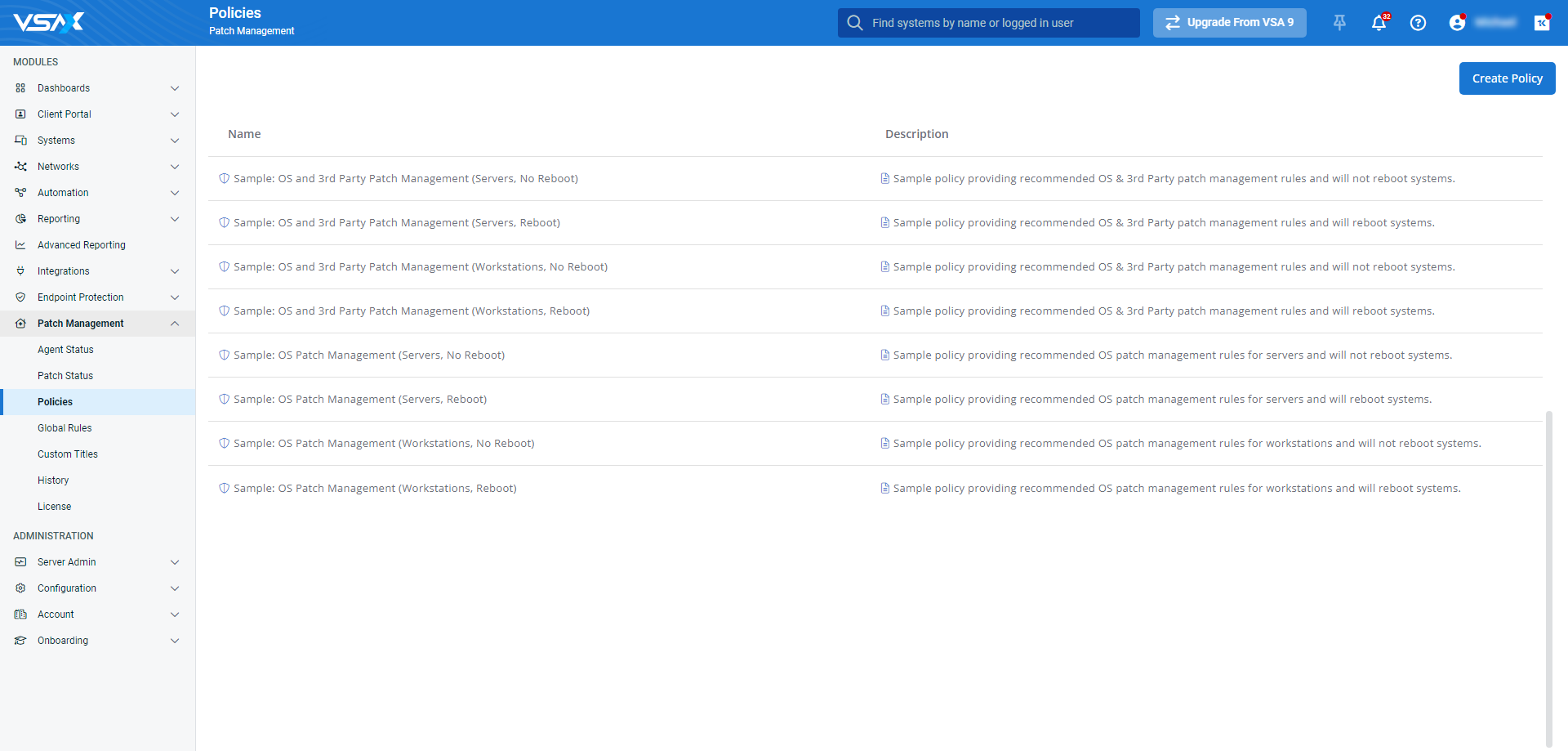
- On the Details page, enter the policy's Name and Description, then choose the policy type from the following options:
- Managed OS and Software Patching: Gives administrators full control over the patching process, including scheduling deployments, approving updates, and defining custom rules. Ideal for environments where strict change control and staged deployments are required.
- Automatic OS and Software Patching: Gives administrators full control over the software patching process, including scheduling deployments and defining custom rules. Configures environments to use native OS patching for operating system updates.
- Click Next to configure the policy Settings. Expand the Settings section below to view details on each settings module.
- Once your policy settings are defined, click Create.
The Settings window contains the configuration settings for the patch management policy. These settings are split into individual configuration modules, each of which handles a different aspect of the patch management policy. The following patch management modules are configurable:
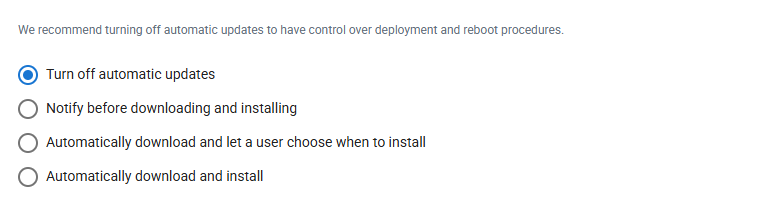
- Automatic Updates: Configure how Windows automatically downloads and installs updates. Manage user notification settings and balance between user control and automation.
NOTE This module is available only for the Automatic OS and Software Patching policy type
- Windows Settings: Customize Windows Update settings, including deferring updates and controlling which update types are installed across managed devices.
- WSUS Configuration: Configure WSUS server settings, if needed.
- Windows Delivery Optimization: Control bandwidth usage and peer-to-peer delivery settings to optimize Windows Update downloads across corporate networks.
- Backup Settings: Configure backup settings to ensure critical data is regularly saved and can be restored in case of data loss or system failure.
- Deployment Schedule: Define and configure the installation of approved updates to minimize disruption and ensure they are applied during scheduled maintenance periods.
- Reboot Schedule: Automate reboot behavior after updates are installed, including setting reboot delays, active hours, and user notifications.
- Notifications: Configure notification settings to keep users informed about available updates and installation errors, ensuring end users are properly informed.
- OS Rules: Define rules for managing operating system updates. Specify which types of updates to install, defer, or ignore based on your organization's needs.
NOTE This module is available only for the Managed OS and Software Patching policy type
- Software Rules: Define rules for managing third-party software updates. Specify which software to install, keep up to date, or uninstall based on your organization's needs.
Select one of the options above or read below to learn more about patch management policy modules.
In the Automatic Updates module, configure how Windows automatically downloads and installs updates, whether users are notified, and if users can choose when to install patches.
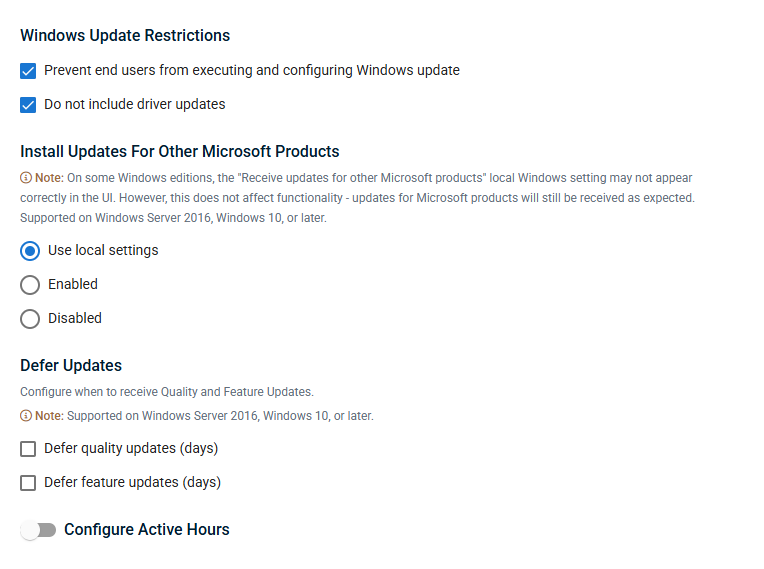
In the Windows Settings module, configure Windows Update restrictions, select if updates for other Microsoft products should install when patching devices, and configure update deferral for Quality and Feature updates.
The following settings are available for configuration:
| Setting | Definition |
|---|---|
|
Windows Update Restrictions |
Configure Windows update restrictions from the following options:
|
| Install Updates for Other Microsoft Products |
Configure install behavior for non-OS Microsoft products from the following options:
|
| Defer Updates |
Configure update deferral settings from the following options:
|
| Configure Active Hours | Configure the maximum number of hours from the start time that users can set their active hours. Windows will not reboot a device for updates during these hours. |
In the WSUS Configuration module, configure your internal update server, if one is present.
Windows Server Update Service (WSUS) functions as an internal update server on your network, hosting updates from Microsoft Update to distribute them to your organization's devices.
The following settings are available for configuration:
| Setting | Definition |
|---|---|
| Use local settings | Does not enable, disable, or change any locally configured WSUS settings. |
| Enabled |
Enables WSUS with the following parameters:
|
| Disabled | Disables WSUS. |
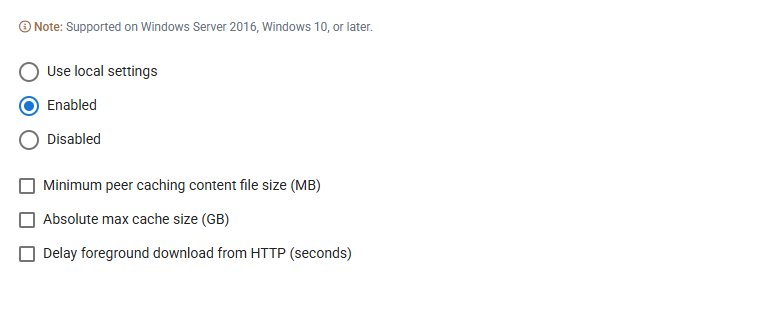
The Windows Delivery Optimization module enables configuration of bandwidth usage and peer-to-peer delivery settings to optimize Windows Update downloads across corporate networks.
| Setting | Definition |
|---|---|
| Use local settings (default option) | Does not enable, disable, or change any locally configured Windows Delivery Optimization settings. |
| Enabled | Enables Windows Delivery Optimization. Check one or more of the below options to configure parameters:
|
| Disabled | Disables Windows Delivery Optimization |
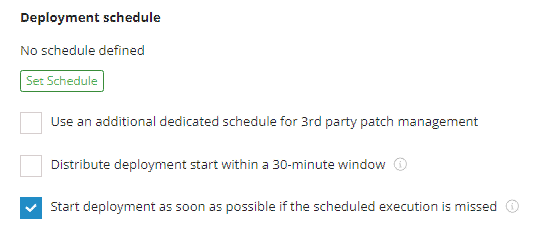
The Deployment Schedule module defines and configures the schedule for when approved updates will install. Customize your deployment schedule to minimize disruption and ensure updates are applied during scheduled maintenance periods.
IMPORTANT The deployment schedule will use the local system time zone of the device being patched.
The following settings are available for configuration:
| Setting | Definition |
|---|---|
| Deployment Window |
Choose the start time of the deployment window. In addition, you can choose to enable either or both of the following settings:
|
| Deployment Schedule |
Configure how often Windows patch deployment should run by configuring the following settings:
|
| Dedicated Software Deployment Schedule |
Configure how often third party software patch deployment should run by configuring the following settings:
|
| Setting | Definition |
|---|---|
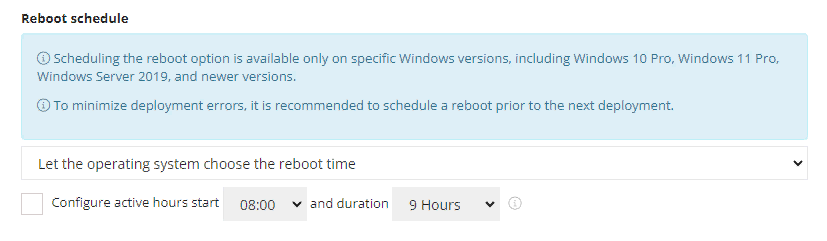
| Let the operating system choose the reboot time |
If selected, Windows schedules the reboot according to working hours configuration and internal logic. If an update requires a restart, Windows will attempt to schedule the restart outside the device's active hours. The system will notify the user about the pending restart and may give the option to postpone or schedule it manually. If the user does not take any action, Windows will restart the system automatically after a grace period, typically within a few days. The exact timing depends on the urgency of the update. If the Windows Automatic Updates are disabled by the policy via Turn off automatic updates, the system will notify user after installation of the update requiring reboot, but the reboot will not occur automatically. You can also choose to configure active hours for devices using this policy by checking the Configure active hours start and duration option in the Windows Settings module. |
| Reboot immediately if required |
As required, immediately reboots the device after installing updates. If you want to notify any logged in users that their devices are going to reboot, check the Notify a logged in user 5 minutes before the reboot option. |
| Schedule the reboot if required |
As required, reboots the device on a specific day or days of the week after installing updates. If you want to notify any logged in users that their devices are going to reboot, check the Notify a logged in user before the reboot option, and set how many hours before the reboot is scheduled that you would like logged in users to be alerted. NOTE Notifications scheduled to go out before patch deployment will only trigger after deployment has finished. NOTE Users will be able to snooze the reboot message or choose to reboot their device immediately, but they cannot delay the scheduled reboot. NOTE If the reboot message occurs within 30 minutes of the scheduled reboot time, users will only be able to choose Restart Now, and will not be able to snooze the message further. If you want to make sure the device just reboots after a certain point at any time, and not just at the specific scheduled time, you can check the Reboot as soon as possible if the reboot deadline is missed option. |
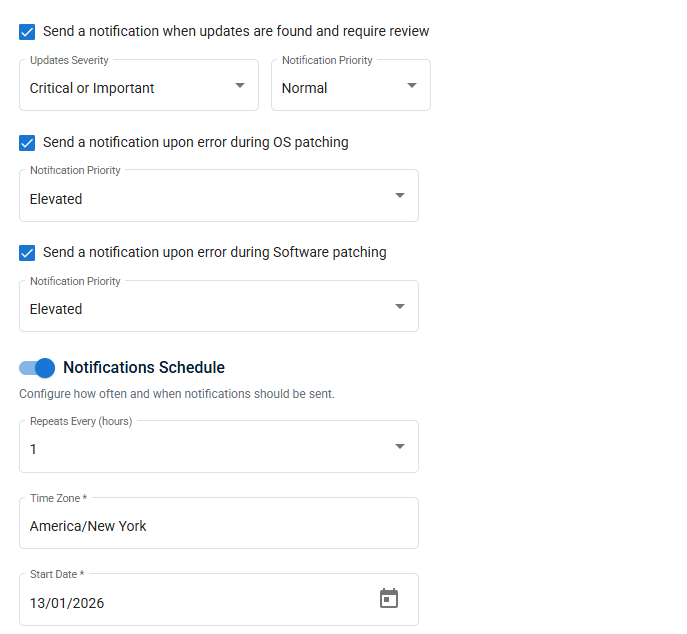
In the Notifications module, configure notification settings to keep users informed about available updates and installation errors, ensuring end users are properly informed.
When setting up these notifications, the following options are available for configuration:
| Setting | Definition |
|---|---|
|
Send a notification when updates are found and require review |
Select the check box to send a notification when update severity and notification priority match the configured settings. When enabled, you can configure the following options:
Refer to OS Rules and Device notifications. |
| Send a notification upon error during OS patching |
Sends a notification when an error occurs when applying a Windows OS patch. When enabled, you can configure the following options:
Refer to OS Rules and Device notifications. |
| Send a notification upon error during Software patching |
Sends a notification when an error occurs when applying a third-party software patch. When enabled, you can configure the following options:
Refer to and Device notifications. |
| Notifications Schedule | Configure how often and when Patch Management notifications will be sent. When enabled, you can configure the following options:
IMPORTANT The notification schedule must be configured in order to receive notifications. The patch scan runs every 3 hours and if it finds a update that you want to be notified on, it will send out the notification per your configured notification schedule. |
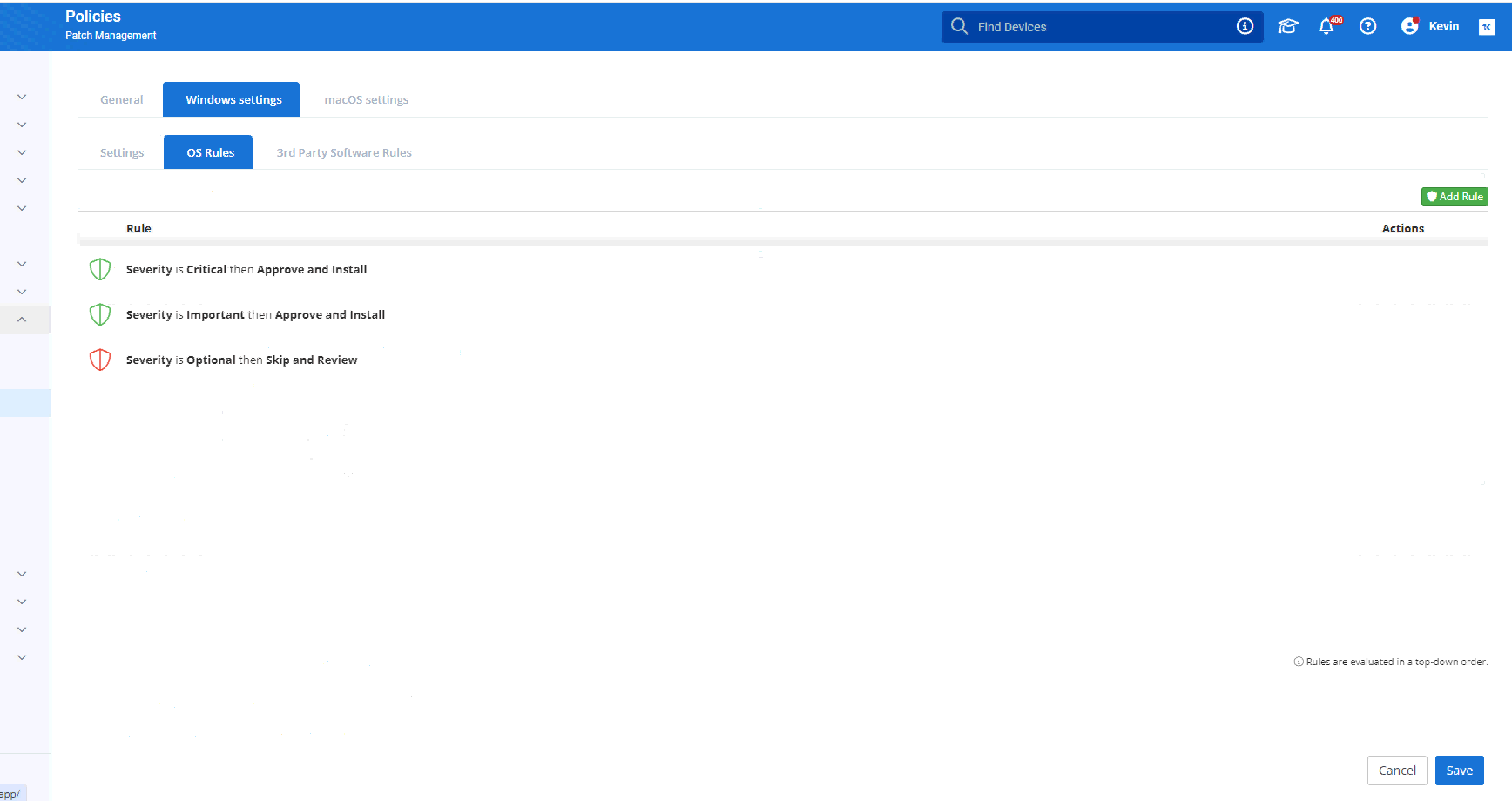
The OS Rules module defines the rules for managing operating system updates. Specify which types of updates to install, defer, or ignore based on your organization's needs. These rules apply in order from the top down.
You can configure VSA 10 to take specific actions based on the following criteria:
| Setting | Definition |
|---|---|
| Severity | Select the update severity from the following options:
|
| Name | Enter all or part of an update's name. |
| Description | Enter all or part of an update's description. |
| Category | Select the update category from the following options:
|
| Days Since Release | Configure how old an update should be to process this rule from the following options
|
| CVE Code | Enter in the CVE (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures) code, allowing you to apply rules to patches based on known cybersecurity flaws. |
| CVSS Score | Enter in the CVSS (Common Vulnerability Scoring System) score, a number between 0.0 and 10.0 that indicates severity of a software vulnerability. This allows you to automatically process patch approval based on known vulnerability severity. |
When an update matches a defined rule, VSA 10 can be configured to take one the following actions:
| Setting | Definition |
|---|---|
| Approve and Install | Approves the patch for installation during the patch deployment window. |
| Skip and Review | Skips the patch but keeps it visible for review, where you can choose whether to approve or reject the patch. Refer to Individual patch rules. |
| Reject and Hide | Rejects the patch and hides it from future review. Refer to How hidden and superseded patches are handled. |
You can add any number of update rules. VSA 10 will evaluate them in a top-down order, and when a rule matches the update, the evaluation will stop and that rule's action will apply. You can click and drag rules using the braille icon on the left to reposition them, or use the arrows on the right to change the rules position.
Good to know
Keep in mind the following limitations about OS rules:
- We recommend using the Managed OS and Software Patching policy type, which turns off automatic updates and enables access to the OS Rules module, to have full control over deployment and reboot procedures.
- Choosing to not install an update is effective only under the following circumstances:
- Within the limited duration of time (between release of the update and forcing of the update) when Microsoft still keeps the update optional; and
- On specific versions of Windows where all updates are optional.
- We do not endorse using scripts to block updates, as doing so can damage your endpoint. They conflict with limitations specifically implemented by Microsoft to ensure that devices cannot automatically block Windows updates.
- While you can script the uninstallation of Windows updates, the updates will be re-installed on the next forced update event, which can cause the cyclical uninstallation and re-installation of system updates.
If a patch is hidden via Reject and Hide based on the OS Rules in a patch management policy, then it is effectively removed from consideration for future updates and won't be reviewed again by the policy, unless the policy rules are changes.
The following behavior is applicable to hidden patches:
- If a patch is hidden, it is not displayed as applicable to the system.
- However, if a hidden patch has superseded another patch that is still applicable, the previous (superseded) patch will be shown instead.
NOTE This follows Microsoft's default behavior.
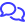
The following example shows what happens when one version of a patch is hidden, but a previous version is not.
- Windows Malicious Software Removal Tool x64 - v5.131 (KB890830) is not installed, and is not hidden:
- Windows Malicious Software Removal Tool x64 - v5.132 (KB890830) is the latest available patch.
- It supersedes Windows Malicious Software Removal Tool x64 - v5.131 (KB890830), which was not installed.
- Windows Malicious Software Removal Tool x64 - v5.132 (KB890830) is not installed, and is hidden:
- Windows Malicious Software Removal Tool x64 - v5.132 (KB890830) is hidden from the list of applicable patches.
- The search then identifies Windows Malicious Software Removal Tool x64 - v5.131 (KB890830) as still applicable and displays it.
Why other tools show different results
- Tools like PSWindowsUpdate and VSA 9 do not support ignoring hidden updates.
- Even if Windows Malicious Software Removal Tool x64 - v5.132 (KB890830) is hidden, these tools will still return it as applicable, though superseded patches won't be shown.
- This difference in behavior leads to discrepancies in the list of visible patches.
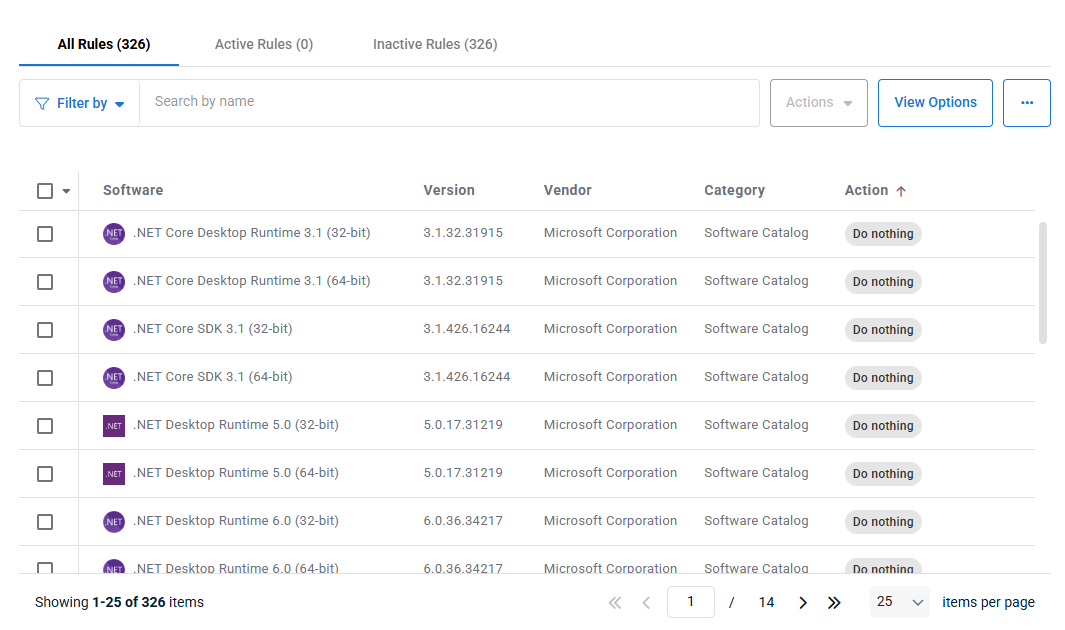
The Software Rules module defines the rules for managing third-party software updates. Specify which software to install, keep up to date, or uninstall based on your organization's needs.
NOTE We manually maintain and continuously update this catalog independently from VSA 10's product releases. To learn about our update process, refer to VSA 10 software application catalog update process and SLAs. For the complete list of supported software applications, refer to VSA 10 software application catalog.
NOTE You can add custom installers to the list of software applicable in this module. Refer to Patch Management custom titles.
To create a rule for a particular application, in the Software column, locate the name of the program or programs you'd like to manage and check the box next to them. You can also select all items on the page or across all pages in the column header. Then, using the Actions menu at the top of the page, select what will happen when the patch management policy runs from the following options:
| Setting | Definition |
|---|---|
| Install and keep up to date | Installs the software and all updates as they become available. |
| Keep up to date | Do not install the software if it is not already present on the device; installs all updates as they become available if it is present. |
| Uninstall | Removes the software from any device where it is present. |
| Do nothing | Takes no action and deactivates the rule. |
You can also customize the view of the software list using the View Options button. The following columns are available:
| Column | Definition |
|---|---|
| Software | Name of the deployable application. NOTE This column is always visible. |
| Version | Current build of the program available from the catalog. |
| Vendor | Name of the software's vendor. |
| Category | Indicates if the software is part of the inbuilt Software Catalog or if it is a user-configured Custom Title. |
| Action | Displays the action that will be performed |
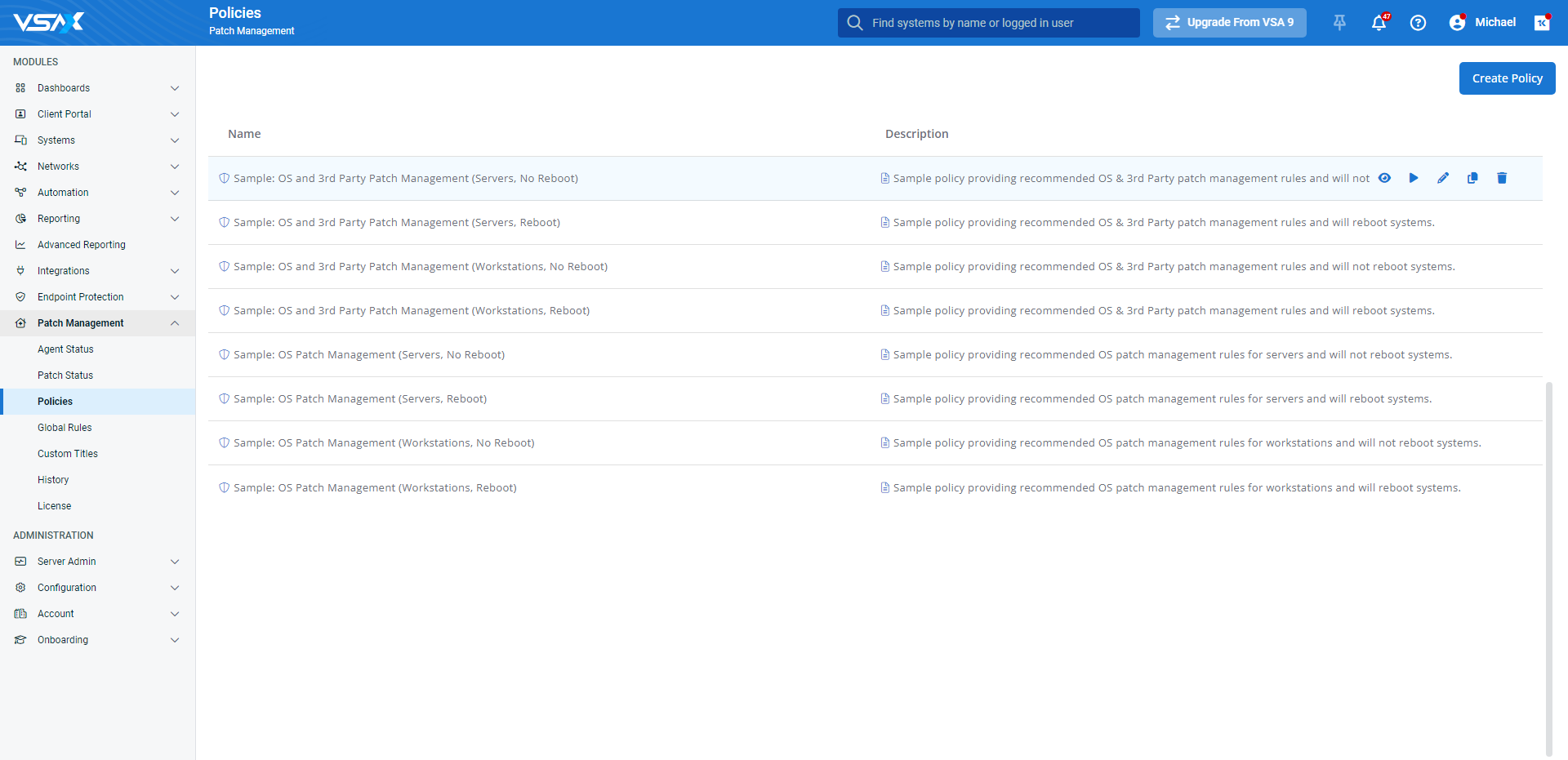
Once the policy is created, it will appear in the table on the Policies page.
Move your mouse over the policy to reveal the following options:
- View
- Run
- Edit
- Clone
- Delete
Before you can use it to manage software, you'll need to assign the policy to a device. To do so, perform the following steps.
- From the left navigation menu in VSA 10, navigate to Patch Management > Agent Status.
- Filter the Agent Status list to the device or devices you'd like to manage.
- To apply a policy to an individual endpoint, move your mouse over its entry in the list and click the
 or
or  icons next to its name. To apply a policy to multiple devices, click Actions > Assign Policy or Actions > Change Policy.
icons next to its name. To apply a policy to multiple devices, click Actions > Assign Policy or Actions > Change Policy. - In the Agent Status modal that opens, select a policy to assign from the drop-down menu. Then, click Assign Policy or Apply Policy Update. You can also assign policies directly to organizations, sites, and agent groups via Configuration > Organizations.
- The selected policy will appear in the Policy column for all selected devices on the Agent Status page.
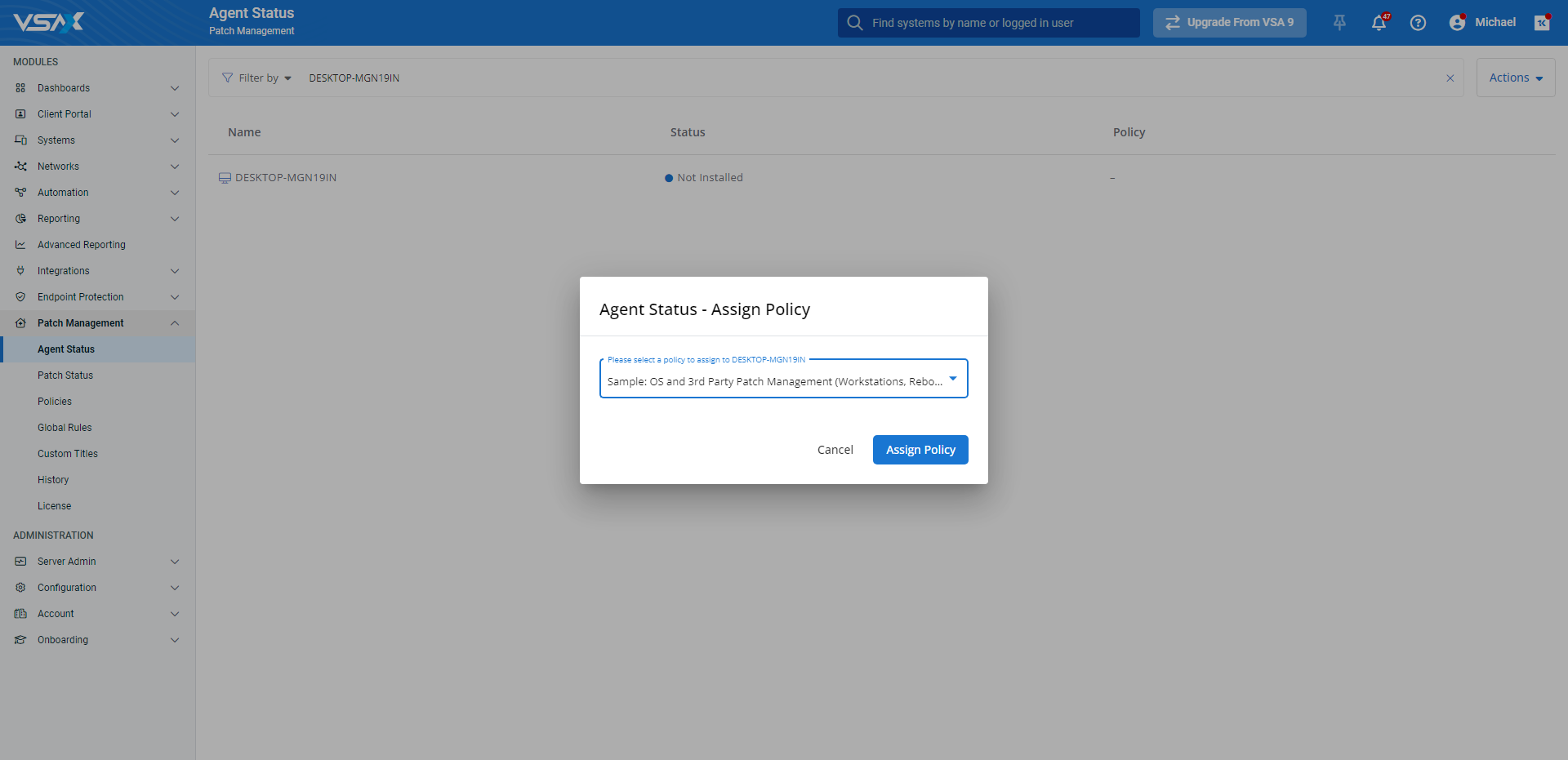
- Once the policy is applied, the status of the selected devices will change to Active.
- To run the policy for an individual device, move your mouse over the selected endpoint's entry in the list and click the
 icon. To run the policy for multiple devices, click Actions > Run Policy.
icon. To run the policy for multiple devices, click Actions > Run Policy.
If you don't currently have a third-party patch management license, you can begin a trial via Patch Management > License. Click the Activate Trial option to gain access. Allow a few minutes for your VSA subscription to update after doing so.