Automating patch review
NAVIGATION Modules > Patch Management > Global Rules
NAVIGATION Modules > Patch Management > Policies
NAVIGATION Modules > Patch Management > Patch Status
VSA 10's Patch Review feature makes it easy to configure automation that intelligently approves or rejects the delivery of OS updates to your managed endpoints. By doing so, you increase the efficiency of your review process by eliminating manual work while maintaining security.
This article provides an overview and use cases for the feature. It also describes how to navigate and customize each tier of the review process.
Overview
During operating system patching, VSA 10 scans potentially-eligible endpoints in real time and assesses the patches against configured rules that you define. VSA 10 has three levels of rules that comprise Patch Review:
-
Global rules: Tenant-level rules assessed for all patches
-
Patch policy rules: Policy-level rules assessed for all patches within a patch policy
-
Individual patch rules: Patch-level rules assessed for a single patch within a patch policy
Each type of rule must be configured in its own section of VSA 10. To learn how to do so, select a topic to continue.
Configuring rules
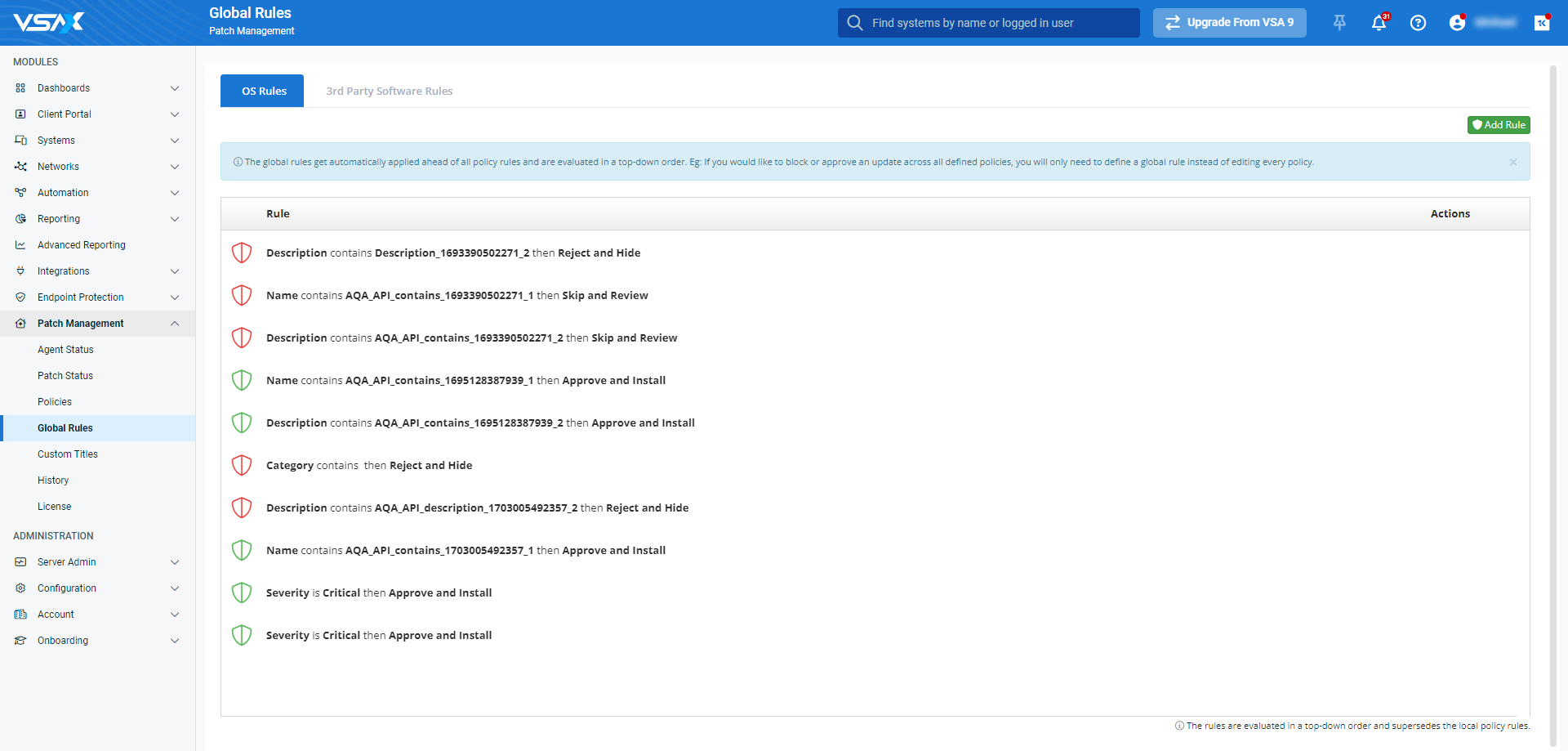
VSA 10 consults these rules first when analyzing a newly-discovered patch. They supersede all other rules and apply in a top-down order. You can set various criteria, such as patch name, description, category, or severity metrics, to approve or reject the patch.
Common use cases for global rules include excluding drivers or patches with known deployment issues. If a patch doesn't meet any global rules criteria, VSA 10 will next evaluate it by patch policy rules.
Global rules are configurable via Patch Management > Global Rules.
For more information, refer to Patch Management global rules.
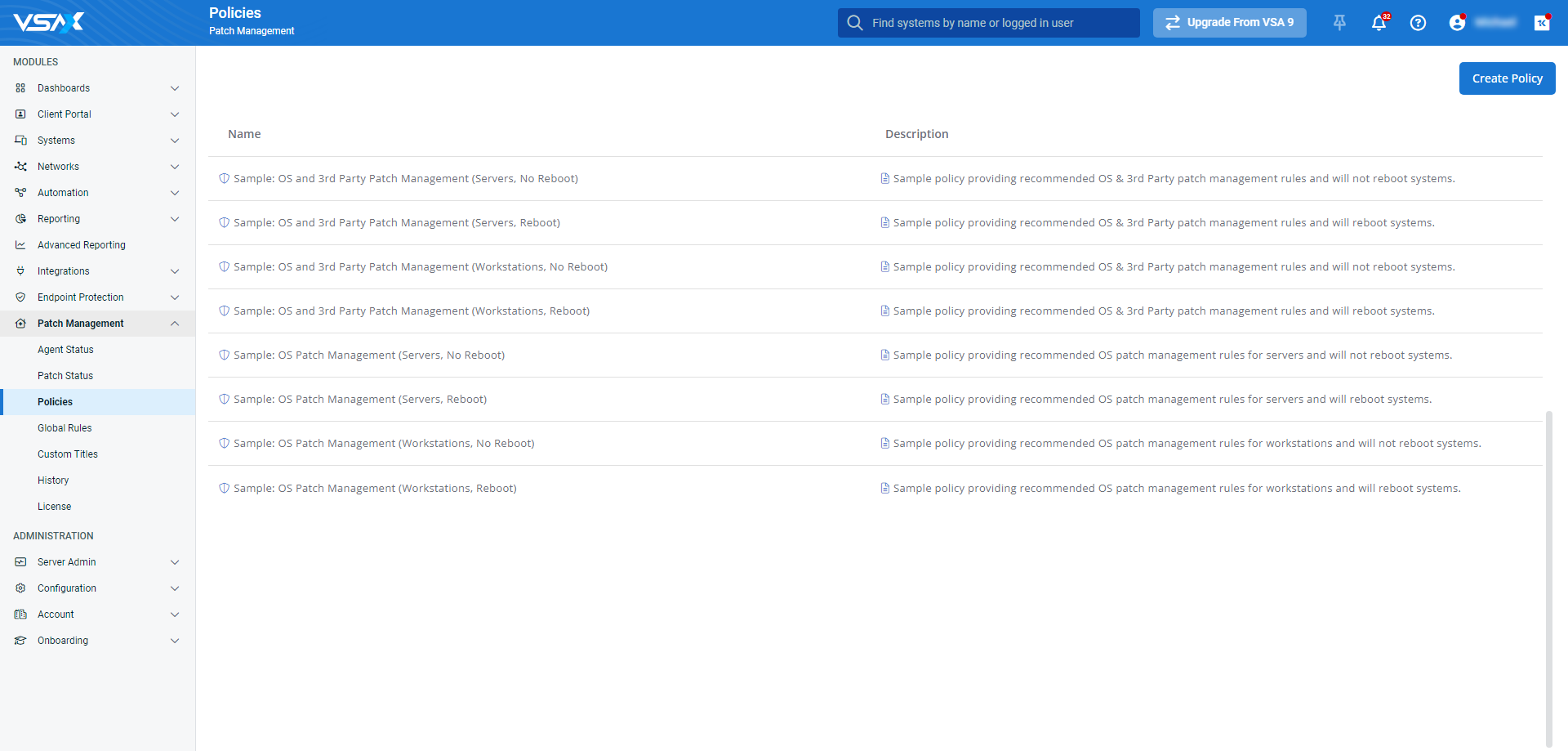
To view and manage patch policy rules, navigate to Patch Management > Policies. Then, click Windows settings and select OS Rules.
Patch policy rules are useful when creating patching strategies for individual organizations or devices with specific needs. For example, you can automatically approve patches if they have CVSS scores that adhere to an organization's security policies. Or, you can defer patch installation for devices that host vital infrastructure.
The workflows for configuring patch policy rules are similar to those for global rules. They have the same set of criteria to choose from.
NOTE Approve and Install policies and Global rules may override the Hide action for a given patch.
If a patch does not match any of the global or patch policy rules, then you'll need to manually review it on the Patch Status page. To learn more, refer to the Individual patch rules section of this article.
Individual patch rules apply when a patch does not match any global or patch policy rules. They are manual actions taken by technicians who have reviewed the patch and have made a decision about how VSA 10 should proceed with its deployment. The manual review process is frequently leveraged by managed service providers (MSPs) and organizations where patches require multi-step approval and testing before full deployment.
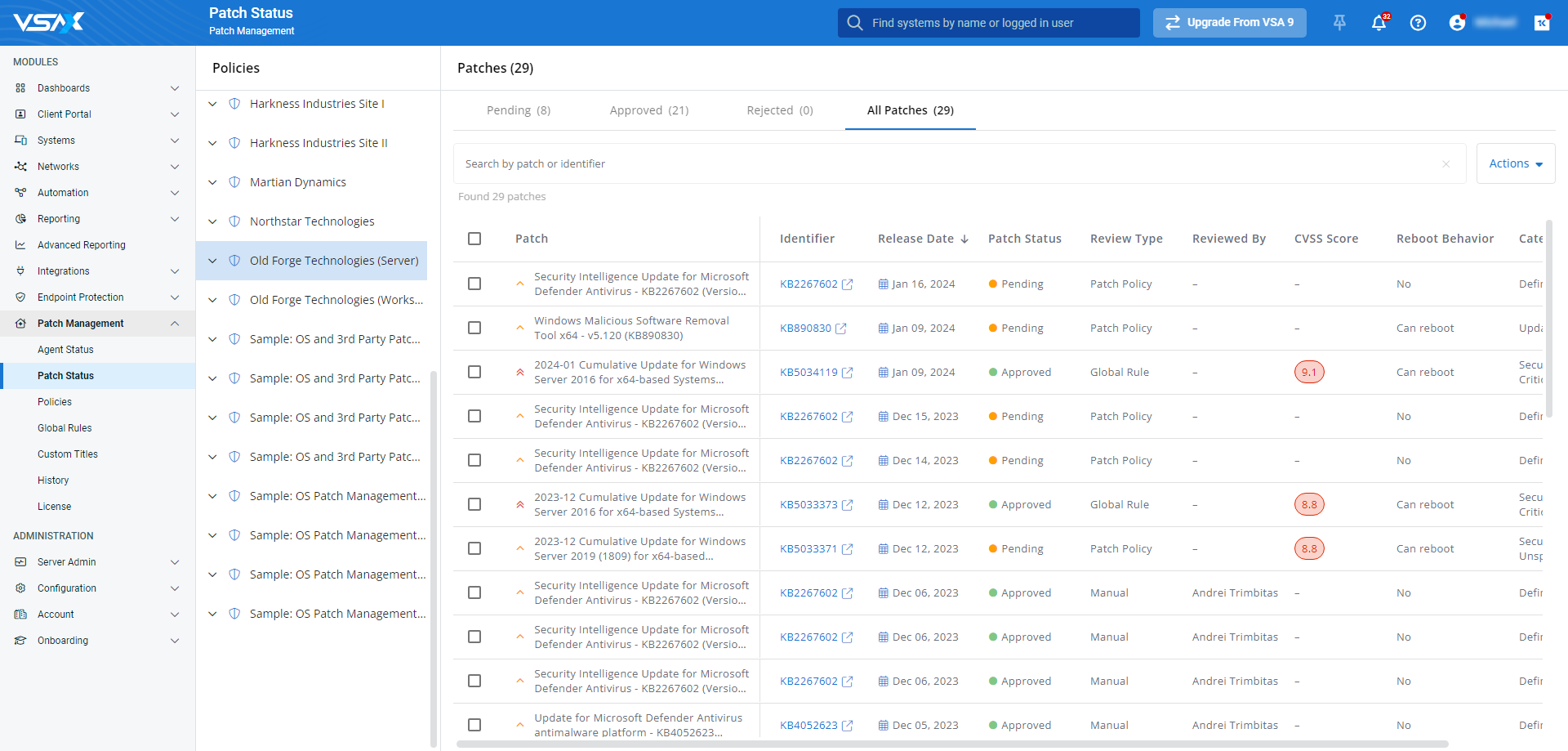
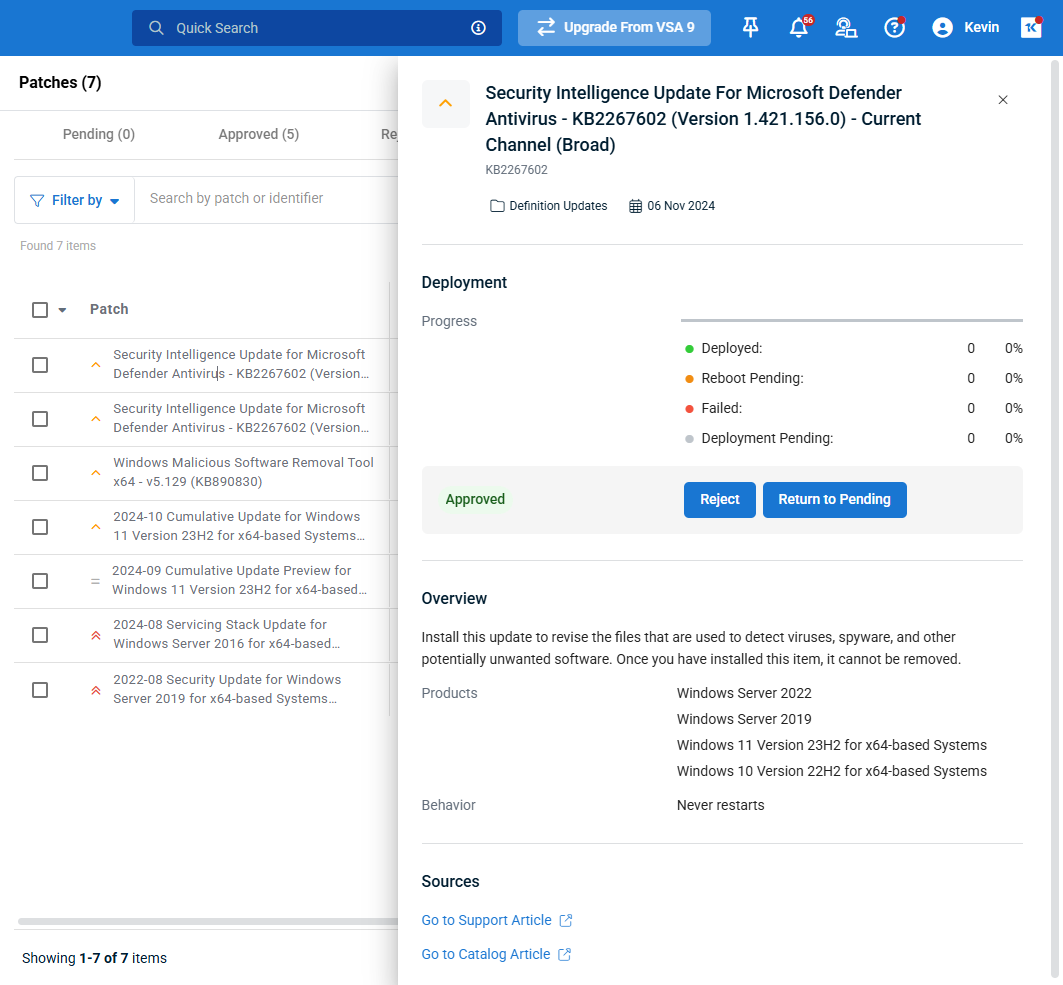
By navigating to Patch Management > Patch Status, you can view a list of all available patches in use in your environment, grouped by policy. The detail view for each policy includes patch review status tabs, enabling you to filter the list by the following patch statuses:
- Pending: Displays all patches for the selected policy that are pending installation approval.
- Approved: Displays all patches for the selected policy that have been approved to be installed.
- Rejected: Displays all patches for the selected policy that have been rejected for installation.
- All: Displays all patches for the selected policy
Clicking any patch surfaces its extended details, severity metrics, pending installations, and links to relevant Microsoft resources in a slide-out Patch Card. This card contains details presented is an aggregate of useful data, including information about the patch and its deployment progress.
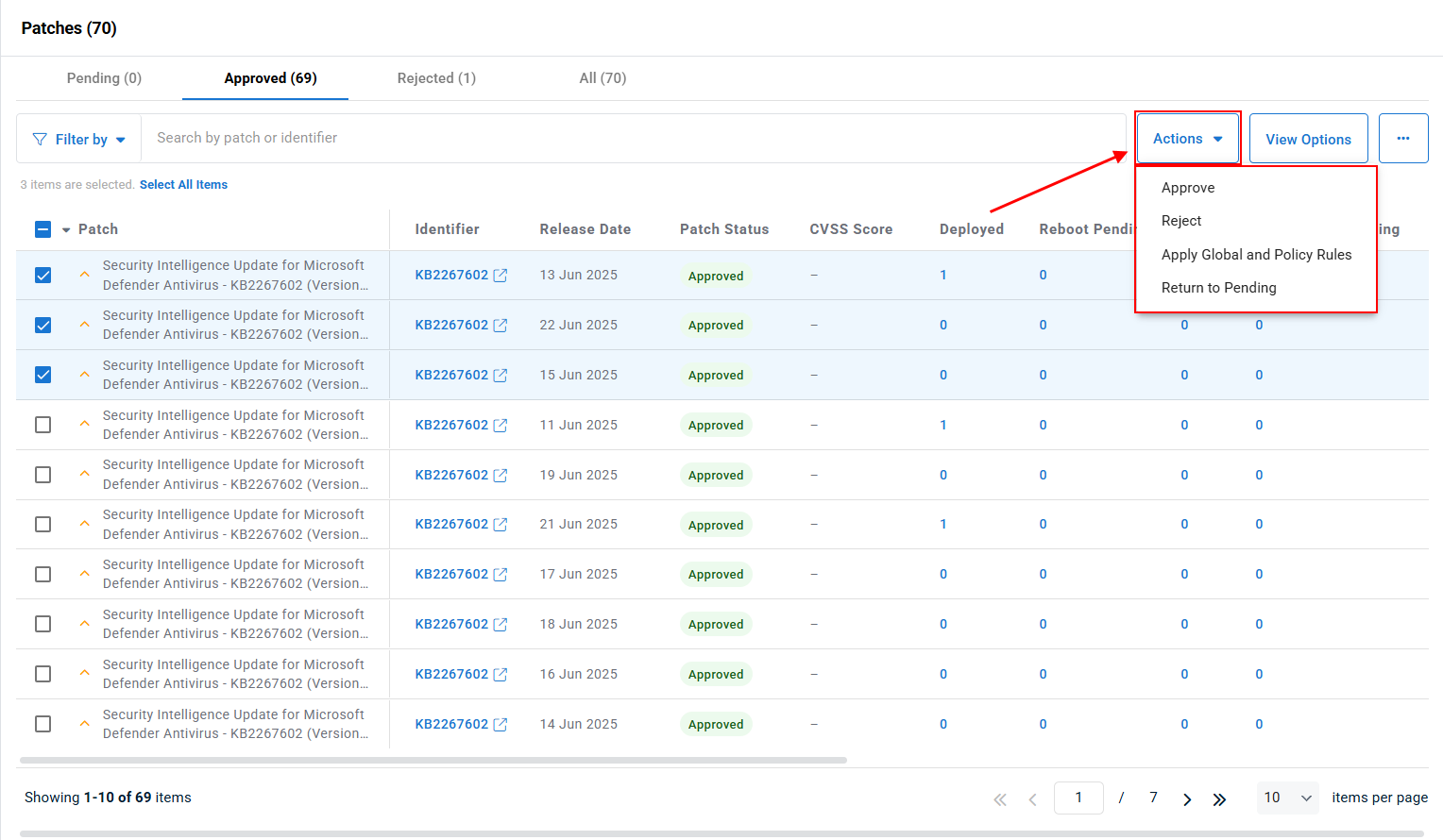
The patch status is automatically determined by the rules within the patch policy and the Global Rules page, but you can either approve or reject the patch's use from the policy's Actions menu in the upper right.
The following Actions can be used to refine the patch status for each patch:
- Approve: Sets the patch status to Approved for the selected patch(es)
- This action supersedes the patch policy and Global Rules
- This action does not modify the patch policy and Global Rules
- Reject: Sets the patch status to Rejected for the selected patch(es)
- This action supersedes the patch policy and Global Rules
- This action does not modify the patch policy and Global Rules
- A patch with a patch status of Rejected will be hidden on the local device
- Apply Global and Policy Rules: Resets the patch status for the selected patch(es) based on the patch policy and Global Rules
- Return to Pending: Sets the patch status to Pending for the selected patch(es)
- This action supersedes the patch policy and Global Rules
- This action does not modify the patch policy and Global Rules
NOTE Global Rules take precedence over patch policy rules.
IMPORTANT Endpoints with outdated VSA agents (versions below 10.6) will not take into account any manual rules configured on the Patch Status page. They will only follow Global and Patch Policy rules.
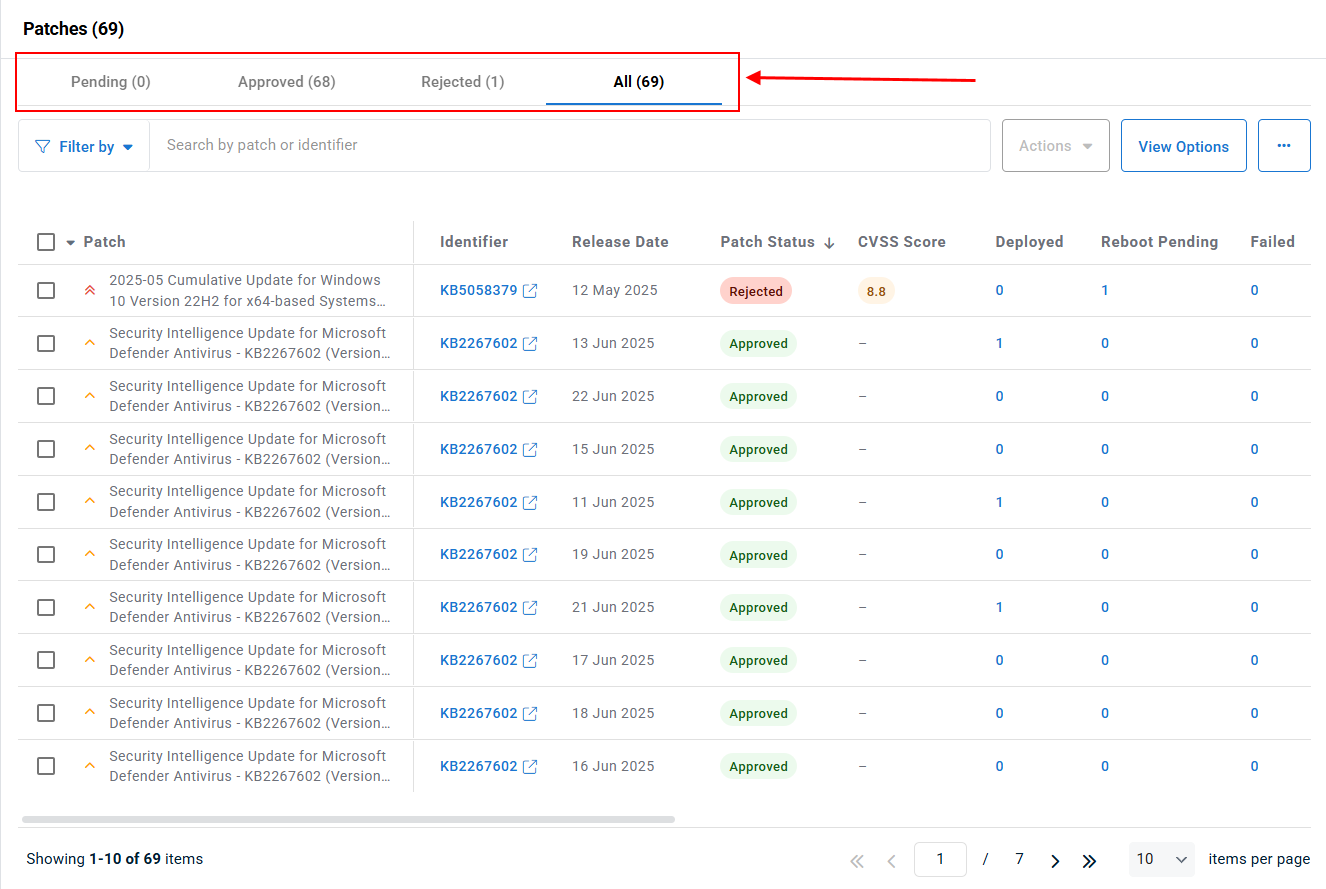
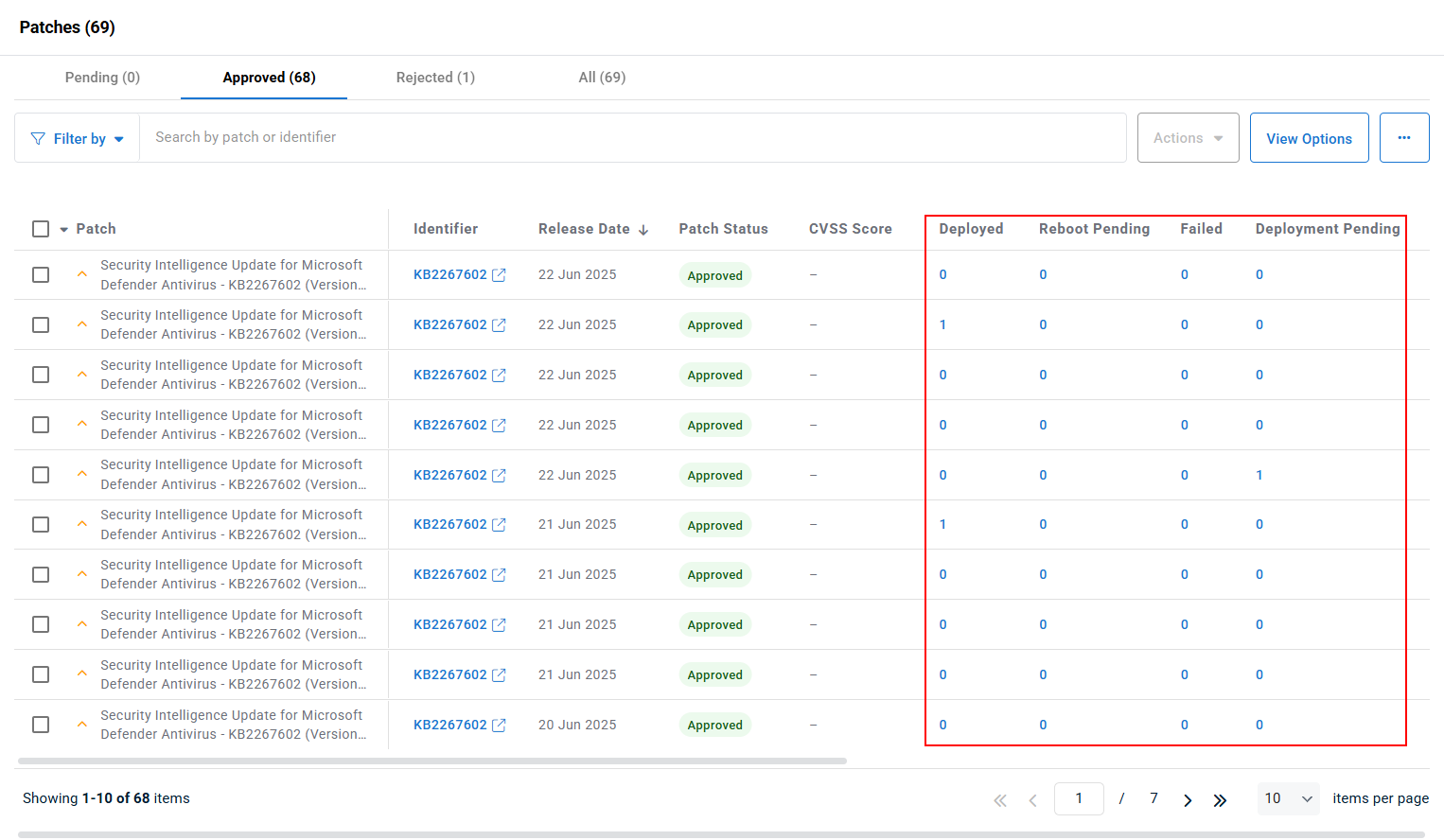
In Patch Management > Patch Status, when reviewing the lists of patches, the number of devices that each patch applies to is displayed, organized into separate sortable columns based on patch deployment status. There are four patch deployment statuses:
- Deployed: The patch has been successfully deployed.
- Reboot Pending: The patch has been deployed but requires a reboot to complete the installation.
- Failed: The patch has failed to deploy.
- Deployment Pending: The patch is available but has not yet been deployed.
Clicking on the count of devices listed under a deployment status will open a list showing all devices where that status applies for that patch.
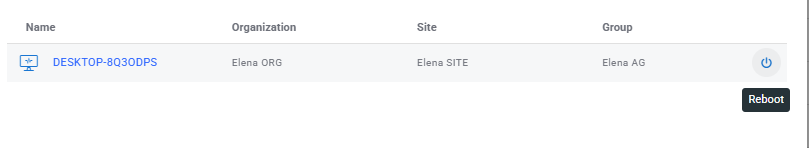
These device lists are filterable, and display data columns and actions appropriate to the status:
- Deployed: device name, organization details and deployment date.
- Reboot Pending or Deployment Pending: device name and organization details, with a hover action to Reboot Now.
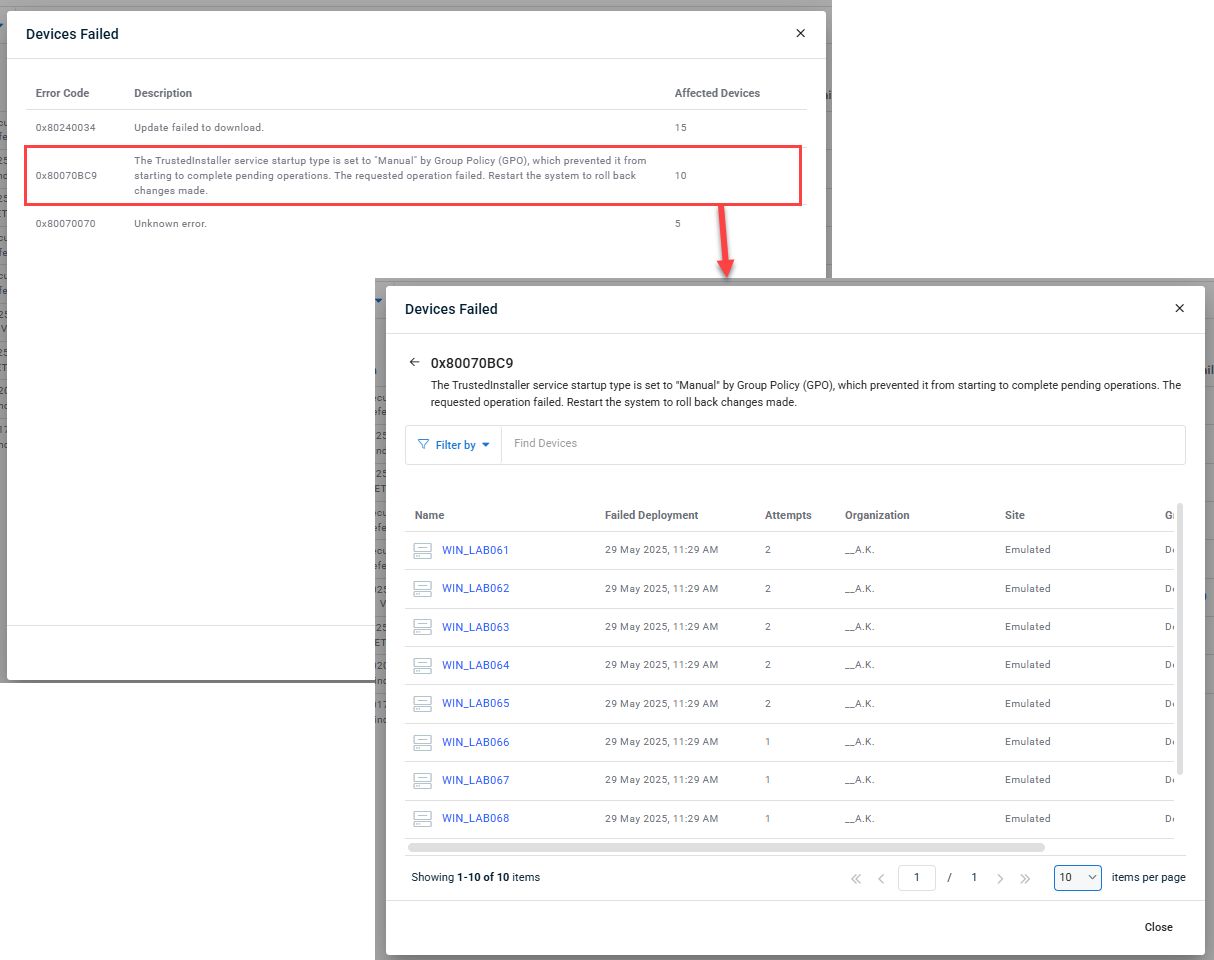
- Failed: The Failed status view is grouped by error message, and in descending order by number of affected devices, so that technicians can quickly identify the most common issues and click through to a list of devices affected by each error. The device view shows device name, organization details, last attempted deployment date and number of attempts, with hover action to Reboot Now.
Learn more
For a comprehensive guide to creating and deploying patch policies, refer to Creating/editing Patch Management policies.